A chalazion is a common eye condition that can cause discomfort and visual disturbances. While it often resolves on its own, understanding its underlying causes, symptoms, and risk factors is crucial for effective management and prevention.
What is a Chalazion?
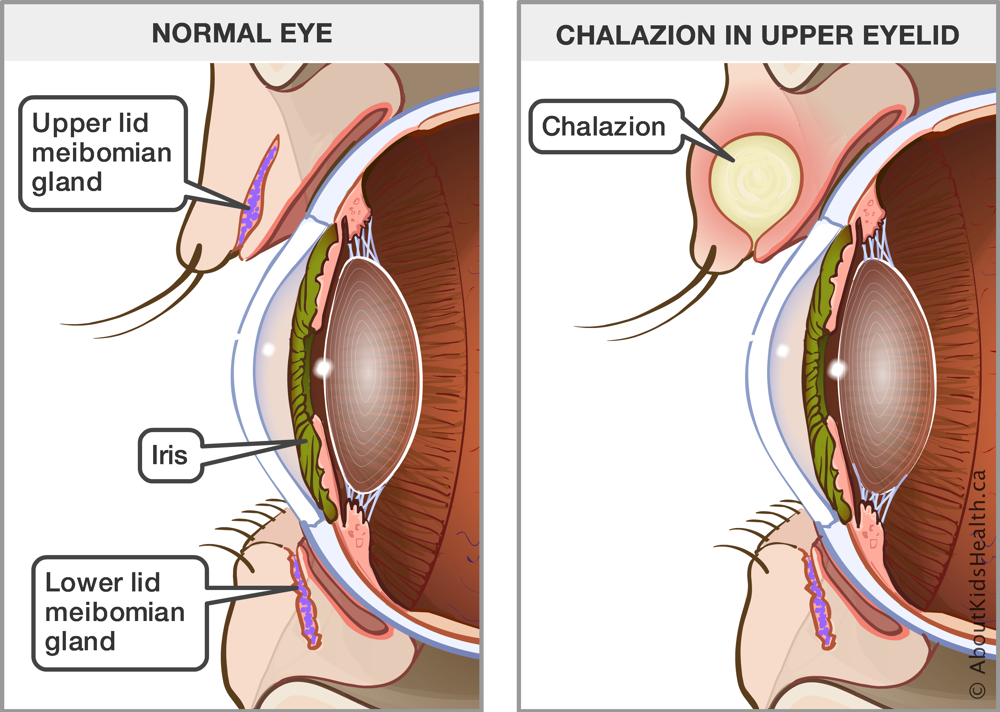
A chalazion is a small, localized swelling in the eyelid resulting from the blockage of a meibomian gland, which is responsible for producing the oily component of tears. Unlike a stye, which is an infection of the eyelash follicle, a chalazion is usually non-infectious and develops over time.
Causes of Chalazion
Chalazia can develop due to several reasons, including:
- Blocked Glands: The primary cause is the blockage of the meibomian glands. These glands can become obstructed due to thickened oil or debris, preventing proper drainage.
- Inflammation: Conditions like blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid) can lead to an increased risk of chalazion formation. The inflamed glands may produce thicker secretions, which are more prone to blockage.
- Skin Conditions: Certain skin disorders, such as seborrheic dermatitis or acne rosacea, can contribute to the development of chalazia by affecting the skin around the eyes and the oil glands.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions may cause inflammation and swelling in the eyelid, increasing the likelihood of gland blockage.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate eyelid hygiene can lead to debris accumulation, raising the risk of blockage.
Symptoms of Chalazion
The symptoms of a chalazion can vary in severity and may include:
- Swelling: The most noticeable symptom is a firm, painless lump on the eyelid. It may start small and gradually increase in size.
- Redness: Surrounding tissue may become red and inflamed, particularly if there is secondary inflammation.
- Discomfort: While chalazia are typically painless, some individuals may experience mild discomfort or tenderness, especially if the chalazion presses against the eyeball.
- Tearing: Increased tear production can occur if the chalazion affects the normal function of the eyelid.
- Vision Changes: In larger cases, the chalazion can cause visual disturbances by obstructing the line of sight.
Risk Factors for Chalazion
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing a chalazion:
- Age: Chalazia are more common in adults but can occur at any age.
- Previous Eyelid Conditions: Individuals with a history of chalazia or other eyelid conditions are at higher risk.
- Skin Conditions: Those with skin disorders like acne or dermatitis may be more susceptible due to oil gland dysfunction.
- Poor Hygiene Practices: Neglecting proper eyelid hygiene, especially in individuals who wear makeup or contact lenses, can lead to increased risk.
- Stress and Fatigue: Chronic stress and lack of sleep can impact the immune system and contribute to eyelid inflammation.
Chalazion Treatment
While many chalazia resolve spontaneously, several treatment options can facilitate healing or provide relief:
- Warm Compresses: Applying a warm compress to the affected eyelid several times a day can help soften the hardened oil, encouraging drainage.
- Gentle Massage: After applying a warm compress, gently massaging the area may help to promote drainage from the blocked gland.
- Medications: In some cases, a doctor may prescribe topical antibiotics or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
- Surgical Intervention: For persistent or large chalazia, a minor surgical procedure may be necessary to drain the fluid and relieve symptoms.
- Preventive Measures: Regular eyelid hygiene, including cleaning with diluted baby shampoo or specialized eyelid scrub pads, can help prevent future occurrences.
How To Get Rid Of Chalazion Without Surgery
Homeopathy is the best way to rid of from chalazion without surgery, there are multiple medicines available in homeopathy for chalazion.
Homeopathy Treatment Of Chalazion
Homeopathy offers various remedies that may help manage chalazion symptoms, aiming to address both the local symptoms and the underlying predispositions. Here’s a detailed overview of potential homeopathic treatments and remedies for chalazion.
Principles of Homeopathy
Homeopathy is based on the principle of “like cures like,” where substances that cause symptoms in a healthy person can treat similar symptoms in a sick person. Homeopathic remedies are highly diluted and customized based on individual symptoms and overall health.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for Chalazion
- Calcarea Fluorica (Calcium Fluoride)
- Indications: Often used for hard, painless swellings. It can help with chronic chalazia that do not resolve easily.
- Dosage: 6X to 12X potency, taken 3-4 times a day.
- Silicea (Silica)
- Indications: Recommended for individuals with a tendency for slow healing and the formation of abscesses or lumps. It is often useful for chronic conditions.
- Dosage: 6X or 30C potency, taken 2-3 times a day.
- Hepar Sulphuris Calcareum (Hepar Sulph)
- Indications: Useful when there is a sensation of pain, tenderness, or inflammation associated with the chalazion. It may help if there is an infection or pus formation.
- Dosage: 30C potency, taken 2-3 times a day.
- Pulsatilla (Anemone Pulsatilla)
- Indications: Indicated for individuals with a changeable nature and a tendency to emotional symptoms. It can help in cases where the chalazion is accompanied by emotional stress.
- Dosage: 30C potency, taken 1-2 times a day.
- Belladonna (Deadly Nightshade)
- Indications: Helpful for acute inflammation, characterized by redness and swelling. Useful in the early stages when the chalazion is more inflamed.
- Dosage: 30C potency, taken 2-3 times a day.
- Thuja (Arborvitae)
- Indications: Beneficial for skin conditions and growths, including cysts and warts. It may help with recurrent chalazia.
- Dosage: 30C potency, taken 1-2 times a day.
